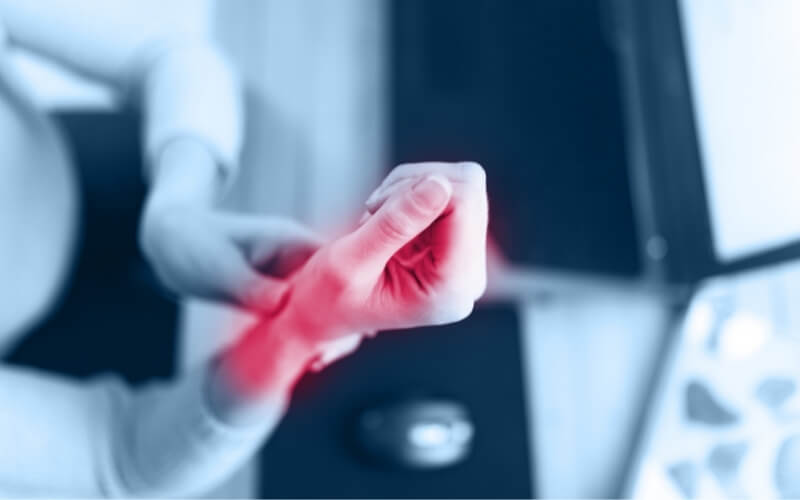
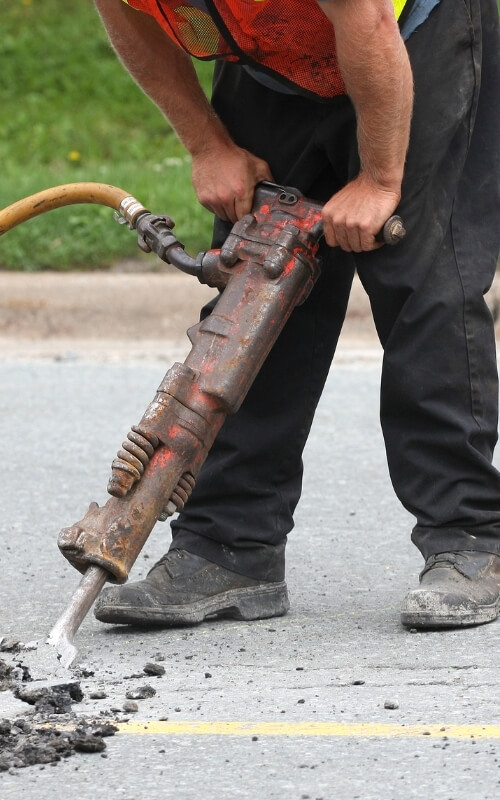
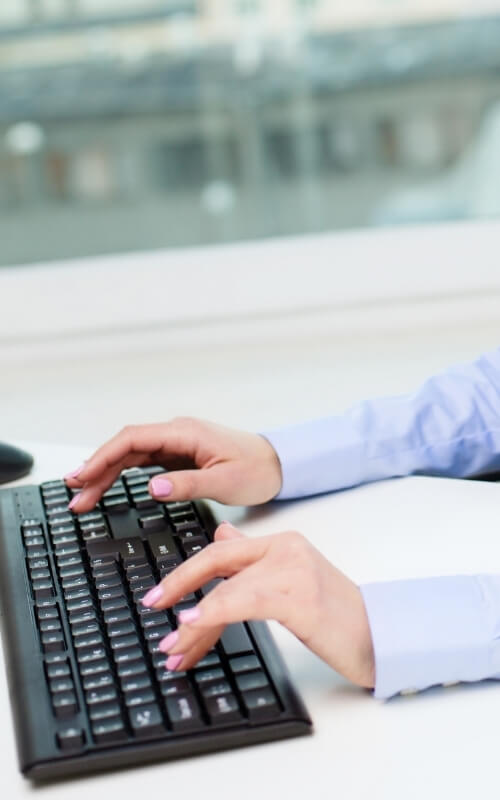
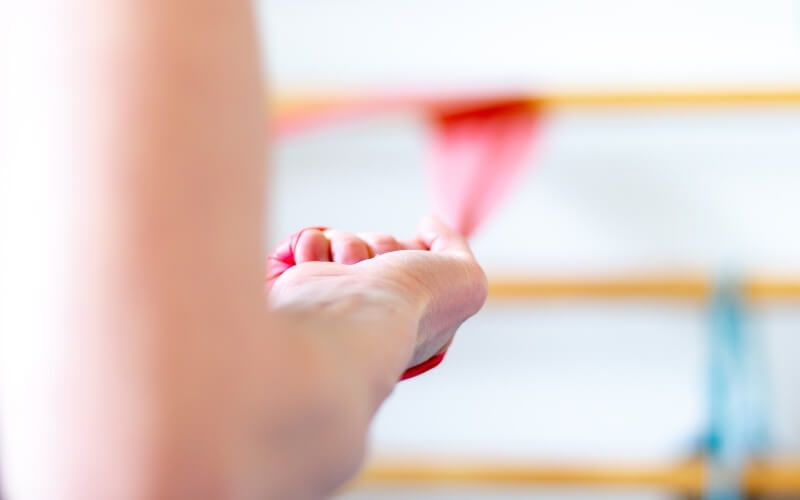
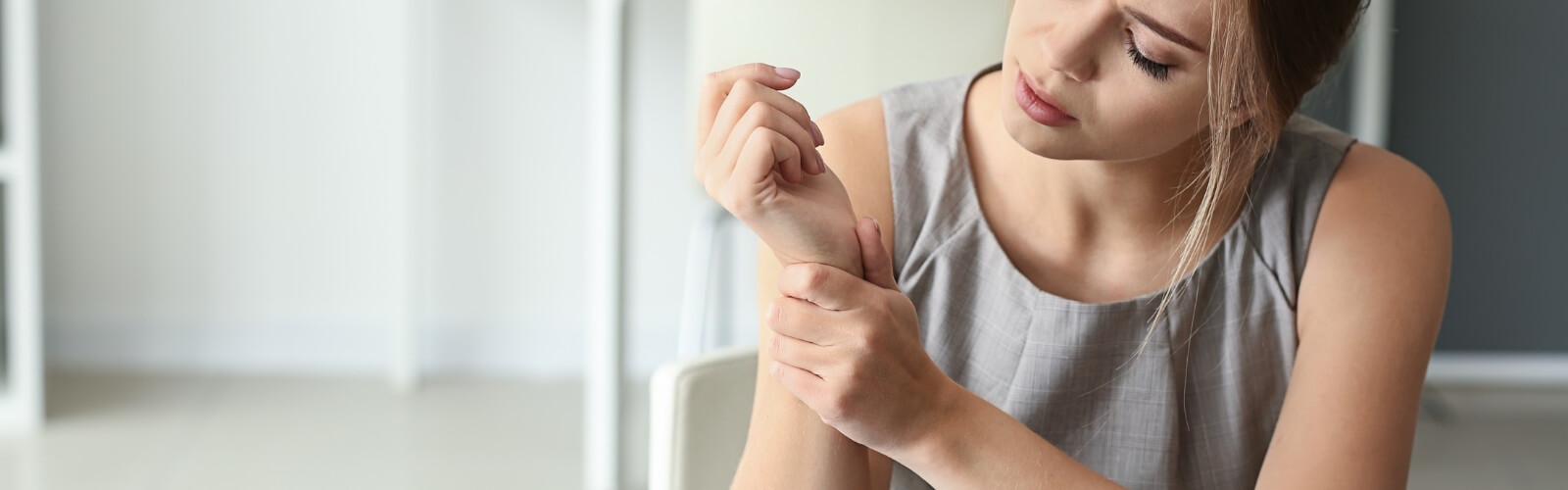
What is Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)?
Repetitive strain injury, a name not given to a specific injury, but rather an umbrella term for a group of injuries caused by repetitive use of a single part of the body.
All areas of the body that involve joint movements are prone to RSI, but it’s most commonly diagnosed in the hands and wrist. This is because we use our hands for most of our daily activities, whether it be hammering a nail, kneading dough or typing this blog post.
Often the strain causes injury to the involved tendon or the underlying joint.
How Do Repetitive Strain Injuries Occur?
It seems like a silly question because there’s an obvious answer – repetitive strain injuries are caused by repetitive strain. But it’s an important question to ask.
Sometimes there’s a simple solution – stop the repetitive action and your pain will settle down. But it’s not always so obvious. RSI can be caused by intrinsic factors such as muscle strength/endurance, and extrinsic factors like posture and desk set up.
By understanding the factors contributing to your injury, you’ll be able to remove the cause and allow the body to heal.
Some of the more common causes of RSI include:
- Sustained postures – particularly in office workers who don’t have an ergonomic desk setup
- Prolonged, sustained positions – such as holding both arms on the steering wheel during long drives
- Use of power tools or vibrating machinery – most commonly jackhammering or drilling
- Tasks involving repetitive force – such as hammering nails or lifting weights
- Direct pressure onto a particular area of the body – commonly seen with repetitive heel striking during running
- Tasks that involve heavy lifting or carrying – such as digging holes or moving soil
What Are The Symptoms Of RSI?
The symptoms of RSI can vary depending on the area of injury and the severity of the strain. Specific areas of the body may respond differently because of the local anatomy and our ability to modify our environment for the injury.
For example, repetitive overload in the wrist can cause a nerve irritation in the carpal tunnel which leads to symptoms of numbness, burning, swelling and heaviness in the hand.
When compared to repetitive strain of the forearm which loads a tendon (such as with golfer’s elbow), your repetitive strain will give you symptoms of pain and weakness.
How To Prevent Repetitive Strain Injury?
The best method of improving your outcomes with RSI is to prevent it from occurring in the first instance. In many cases this will simply involve taking more regular breaks or longer breaks so that your body can recovery from the load that’s it has undertaken.
In instances where external factors are placing additional stress on your body, changing these to reduce stress can make a big difference to your risk of injury. For example, using tools that are too large for your hand size will force you to adopt a wider grip and place additional strain through the fingers and wrist.
Another example is an office worker who uses a flat keyboard for typing – by not having adequate wrist support additional pressure will be placed onto the wrist for typing.
While these examples seem insignificant, you need to remember that RSI is often developed from multiple minor strains accumulating to become a significant strain.
So, while using a muscle to lift your wrist when typing may not seem like a big deal, performing that same action for 40 hours per week over several months can ultimately lead to RSI wrist.
Intrinsic influences of RSI can also be addressed to prevent future injury. Most often this is seen in people undertaking a new task that they haven’t previously performed.
An example of this is a tradie’s apprentice who has recently come into the workforce. Gradually their body will adapt to the new workload. But a supplementary strengthening program can be an effective way to reduce the risk of injury.
Its also common to see intrinsic risk factors in people with previous injury. Previous injury may cause weakness or stiffness which can contribute to RSI. Treating these longstanding issues may not be successful, but understanding how you can modify the task you’re performing to accommodate for your injury can successfully prevent RSI.
Ultimately, identifying the risk factors that are most relevant to your situation and implementing strategies to overcome them is the most effective way to reduce your risk of developing RSI.
RSI Treatment
The key to treating RSI is to stop the activity that is causing the RSI. However, this is not always as simple as it seems. Often people will struggle to eliminate the cause when it’s related to their work or sports. Speak to your physiotherapist for advice on how you can modify your activity to prevent RSI, rather than completely stopping the activity.
Common self-help options for RSI treatment include:
Stretches
Incorporate a light stretching program into your daily routine. Gaining more flexibility and preventing muscles from tightening up will help reduce your symptoms from RSI.
Improved Posture
Ergonomic settings to improve postures and general body positioning will reduce your onset of RSI. This may involve the use of postural supports, various mouse/keyboard options or stand-up desks.
Load Modification
Take regular breaks. Your body needs these breaks to recovery and replenish the load tolerance of your soft tissues. By breaking up your workload you will significantly reduce your RSI symptoms.
Technological Changes
Use of available technological changes such as dictation software or a touchpad mouse can reduce the load placed on the hands when using the computer. Again, this may seem insignificant in short doses, but in the context of a long working week these changes can make a big difference to your pain.
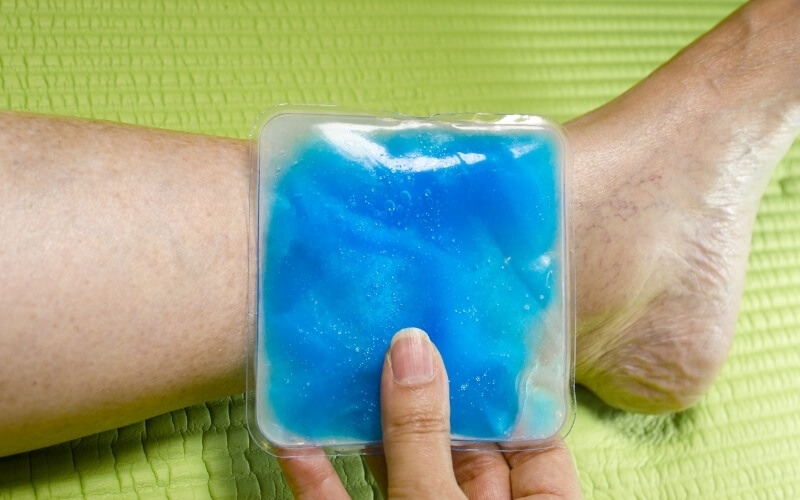
Ice Packs
Although not a cure, ice packs are an effective pain management technique which also helps to prevent the progression of your RSI.
Strengthening
Building both strength and endurance in the affected muscles will help improve the tolerance to loading and reduce RSI symptoms. This is a very difficult process to undertake once RSI has developed, and should only be used under strict guidance of a physiotherapist.
Summary
Your physiotherapist is essential for effective treatment of these conditions. They will provide a detailed assessment to identify and treat your pain, discuss potential causes of the RSI, and provide an adequate long-term rehabilitation strategy to prevent future occurrence of RSI.
Book an appointment with our physio for assistance with your repetitive strain injury.
One-on-One Physiotherapy Care - Complete Attention - You Deserve It !
Contact Us today to find out how we can help you.